Advertisement
Advertisement
Managing Asset Correlations
By:
Intro
It is import to understand that assets movements do not operate in a vacuum. Changes nearly always induce a reaction of some sort, and this is the case
It is import to understand that assets movements do not operate in a vacuum. Changes nearly always induce a reaction of some sort, and this is the case in the capital markets. When there are changes, in the global macro environment, they are usually reflected in the currency market, which then spills over into commodities, equities and debt.
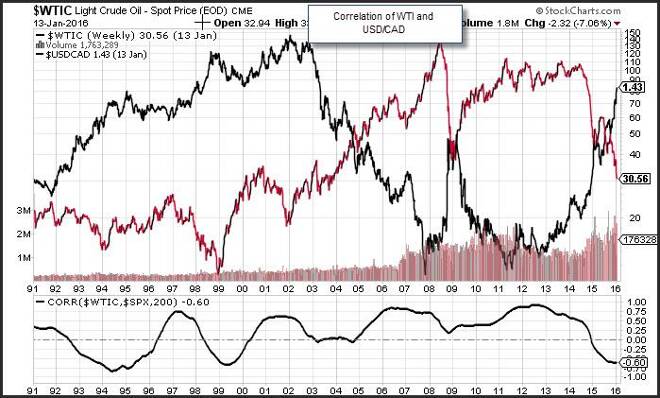
One of the factors that is very important to understand is forex correlations. Forex correlation of currencies gives the forex trader a firm understanding of the risk associated to a combinations of positions. If you are trading the dollar and commodities that are priced in dollar you need to understand that these instrument can move in tandem, and if you are attempting to run a diversified portfolio this is pertinent to your performance.
Forex correlation is a measurement of the relationship between two currency pairs or a currency pair and a commodity or a currency pair and an index. In general correlation measures how much these instrument will move in tandem. So, for example forex correlation gives the forex trader an idea if currency pairs will move in a similar way.
So, when trading currency pairs, a trader needs to evaluate the potential risk of a combination of currency positions, or mixed positions. When trading forex, two correlated currencies will typically have a coefficient which is close to 100% if they move in the same direction. On the other hand, two currencies that move in opposite directions will have a correlation of -100%. The percent is a correlation coefficient, which targets how closely the performance of two assets are over a specific period of time. A correlation coefficient of zero reflects no common movements between two assets.
Correlations are dynamic, which means they are constantly changing. The shorter the period you use to measure correlation they greater the likelihood of a change in the correlation. For example, if you are measuring a correlation over a 1-week period, market noise could change the dynamic between two assets. If the assets are highly correlated, a small window of change would not likely reduce a correlation that is measured over a year. Many traders measure correlation on a moving basis. This means you can constantly measure how dynamic the correlation is over time. It similar in a way to the way you would measure a moving average.
Many forex traders will calculate correlations on their own through the use of tools such as spreadsheets. Excel for example provides a correlation calculation where you can grab historical performances and calculate easily the historical correlation between two or more assets.
In summary, a forex trader needs to understand correlations to be able to evaluate how a portfolio will perform in an effort to manage risk. If you have many securities that are highly correlated, you might be betting on only one direction. It is prudent to have a consistent measurement of the correlation of your assets to generate the best risk adjusted returns.
About the Author
David Beckerauthor
David Becker focuses his attention on various consulting and portfolio management activities at Fortuity LLC, where he currently provides oversight for a multimillion-dollar portfolio consisting of commodities, debt, equities, real estate, and more.
Advertisement